Introduction
I had gotten a joystick a while ago and wanted to do something different and interesting with it. After coming up with and discarding a bunch of other ideas, I came up with the Arduino Sketcher. The ideas was to make something similar to an Etch-a-Sketch but uses the joystick instead of two dials. The computer would serve as the sketching pad while to Arduino relayed all the commands sent by the user. This project uses both Arduino and Python and turned out to be fairly simple to implement.
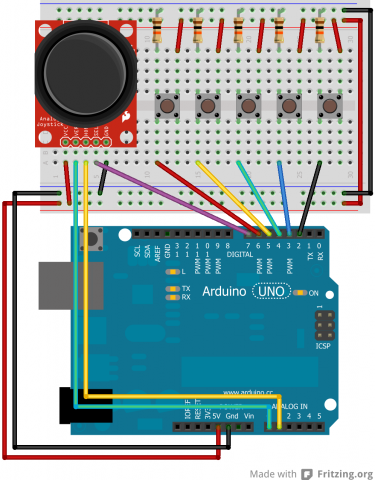
Schematic
Below is the schematic of the Arduino Sketcher.
The sketcher allows the user to click on various parts of the canvas to determine where the lines start out. This allows for disconnected lines. It uses the joystick to determine where to draw the line and how quickly. The more the user shifts the joystick, the faster it draws lines. When the user holds the joystick down, the button triggers and a circle will be drawn on the canvas. The longer the button is held down, the larger the circle is. The buttons next to the joystick allow the user to select various colors indicated by the wire. There are buttons available that are colored and can be used to indicate color.
Code
Arduino Code
Below is the code on the Arduino side. The Arduino is mostly used to translate the controller and send commands to the Python side.
/****************************
Controller for Sketcher
Jennifer Case
13/06/2013
****************************/
//Declare pins
int redPin = 7;
int yelPin = 6;
int grnPin = 5;
int bluPin = 4;
int blkPin = 3;
int verPin = A0;
int horPin = A1;
int circlePin = 8;
int lastColor = 4;
long previousMillis = 0;
long interval = 200;
float numClicks = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(38400);
pinMode(redPin, INPUT);
pinMode(yelPin, INPUT);
pinMode(grnPin, INPUT);
pinMode(bluPin, INPUT);
pinMode(blkPin, INPUT);
pinMode(circlePin, INPUT);
digitalWrite(circlePin, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
//read values from color buttons
int redBtn = digitalRead(redPin);
int yelBtn = digitalRead(yelPin);
int grnBtn = digitalRead(grnPin);
int bluBtn = digitalRead(bluPin);
int blkBtn = digitalRead(blkPin);
//read and normalize values from the potentiameters
float verPos = (analogRead(verPin)-504.0)/504.0;
float horPos = (496.0-analogRead(horPin))/496.0;
//read value of button
boolean circleBtn = digitalRead(circlePin);
//if either normalized value from the joystick is
//essentially zero, make it equal zero
if (verPos < 0.01 && verPos > -0.01) {verPos = 0;}
if (horPos < 0.01 && horPos > -0.01) {horPos = 0;}
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
char charBuf[5];
//if enough time has passed and either potentiameter is not zero,
//print out commands for both axes
if(currentMillis - previousMillis > interval && (verPos != 0 || horPos != 0)) {
Serial.print("X,");
dtostrf(verPos, 4, 2, charBuf); //turn float to string
Serial.println(charBuf);
Serial.print("Y,");
dtostrf(horPos, 4, 2, charBuf); //turn float to string
Serial.println(charBuf);
previousMillis = currentMillis; //reset the interval
}
//determine color and print it to sketcher if it was not the last color
if (redBtn && lastColor != 0) {
Serial.println("C,R"); //print command
lastColor = 0;
}
else if (yelBtn && lastColor != 1) {
Serial.println("C,Y"); //print command
lastColor = 1;
}
else if (grnBtn && lastColor != 2) {
Serial.println("C,G"); //print command
lastColor = 2;
}
else if (bluBtn && lastColor != 3) {
Serial.println("C,B"); //print command
lastColor = 3;
}
else if (blkBtn && lastColor != 4) {
Serial.println("C,K"); //print command
lastColor = 4;
}
//while button on joystick is clicked,
while (!circleBtn) {
numClicks++; //increase counter
circleBtn = digitalRead(circlePin); //read the button again
}
//if numClicks is more than zero,
if (numClicks > 0) {
Serial.print("O,"); //start printing command
numClicks = numClicks/20000.0; //normalize the numClicks
dtostrf(numClicks, 4, 2, charBuf); //int to string
Serial.println(charBuf); //print the rest of the command
numClicks = 0; //reset numClicks
}
}
Python Code
Below is the Python code. It just translates the commands from the Arduino side and draws the appropriate lines on the canvas. It should be noted that this was coded for Python 3.
#! /usr/bin/python
from serial import *
from tkinter import *
import time
#Serial
ser = Serial("COM9",38400,timeout=0,writeTimeout=0)
time.sleep(1)
#initialize positions
xPos = 500
yPos = 300
#function for making a circle
def drawcircle(canv,x,y,rad,color):
canv.create_oval(x-rad,y-rad,x+rad,y+rad,width=0,fill=color)
#function for mouse click
def goToClick(event):
global xPos
global yPos
xPos = event.x
yPos = event.y
#Main window
root = Tk() #Tk is a function that makes a class
root.wm_title("Canvas Sketch")
root.config(bg="#8D8A8A", bd="0")
#make the sketcher canvas
sketcher = Canvas(root, width=1000, height=600, bg='white')
sketcher.grid(row=0, column=0)
sketcher.bind('<Button-1>', goToClick)
#log = Text(root, width=50, height=8, takefocus=0)
#log.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=2, pady=2)
#initializations
color = 'black'
verPos = 0
horPos = 0
def runLoop(event=0):
ln = ser.readline() #get command
lineStr = ln.decode(encoding='UTF-8')
#log.insert('0.0',lineStr)
#print(lineStr)
#initializations
Xline = 0
Yline = 0
circline = 0
newLine = 0
#other neccessary variables
global verPos
global horPos
global xPos
global yPos
global color
#determine selected color
if "C" in lineStr:
for line in lineStr.split(','):
if "R" in line:
color = 'red'
if "Y" in line:
color = 'yellow'
if "G" in line:
color = 'green'
if "B" in line:
color = 'blue'
if "K" in line:
color = 'black'
#get X value
elif "X" in lineStr:
if len(lineStr) > 6: #make sure length is appropriate
for line in lineStr.split(','):
if Xline == 1:
#take value from lineStr
verPos = float(line.strip("\n \r"))*-1 #fix direction
#print(verPos)
Xline = 0
elif Xline == 0:
Xline = 1
#get Y value
elif "Y" in lineStr:
for line in lineStr.split(','):
if Yline == 1:
#take value from lineStr
horPos = float(line.strip("\n \r"))
#print(horPos)
Yline = 0
newLine = 1 #indicates that a line is ready to be drawn
elif Yline == 0:
Yline = 1
#draw circle
elif "O" in lineStr:
if len(lineStr) > 4: #checks length
for line in lineStr.split(','):
if circline == 1:
#gets value
circDiam = float(line.strip("\n \r"))
#draw circle
drawcircle(sketcher,xPos,yPos,5*circDiam,color)
circline = 0
elif circline == 0:
circline = 1
if newLine == 1:
newY = yPos+5*verPos #finds new end position
newX = xPos+5*horPos #finds new end position
sketcher.create_line(xPos, yPos, newX, newY, fill=color, width = 2)
xPos = newX #adjusts end position
yPos = newY #adjusts end position
root.after(10, runLoop)
runLoop()
root.mainloop()