Saving Images on an SD Card
Saving Images on an SD CardIntroduction
Before trying this code, make sure you have ensured that your camera works because you will not be able to see what is happening with the camera while it is saving to the SD card. If you are having issues with this, please check out the Evaluation Software provided by Linksprite.
You should also take a look at this tutorial and ensure that you can in fact get a converted images before trying to save several images.
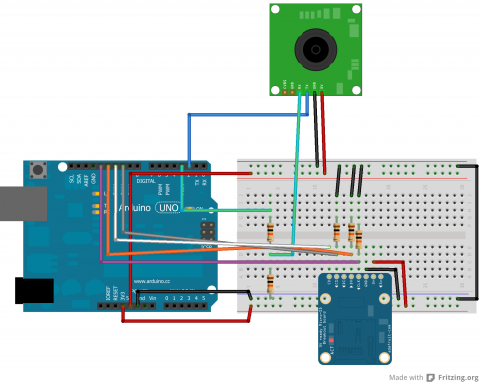
Parts
- TTL Camera by Linksprite
- SD Card Breakout Board
- SD Card
- 2 10k Resistors
- 3 other Resistors (I'm not sure if size matters, but mine were all above 1k)
- Wires
- Arduino
Schematic
Code
Arduino
This code sets up the SD card and takes pictures, incrementing the name the file is saved as each time.
/***************************
Save Images on SD Card
by Jennifer Case
4/14/2014
Parts:
-SD Card Breakout Board
-TTL Camera
Pin 2,3 - Camera
Pin 10 - CS/D3
Pin 11 - CMD
Pin 12 - D0
Pin 13 - CLK
****************************/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <SdFat.h>
//SD Card
SdFat sd;
SdFile myFile;
int picCnt = 0;
//Camera
byte incomingbyte;
SoftwareSerial cameraSerial = SoftwareSerial(2, 3); //Configure pin 2 and 3 as soft serial port
int a=0x0000,j=0,k=0,count=0; //Read Starting address
uint8_t MH,ML;
boolean EndFlag=0;
//Declare pins
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(19200); //start serial
cameraSerial.begin(38400); //start serial with camera
// Initialize SdFat or print a detailed error message and halt
// Use half speed like the native library.
// change to SPI_FULL_SPEED for more performance.
if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt();
SendResetCmd(); //allows camera to take pictures
delay(3000); //delay necessary for camera reset
}
void loop() {
//create title for images
char photoTitle[25] = {};
sprintf(photoTitle, "pic%d.txt", picCnt);
//make sure file can be created, otherwise print error
if (!myFile.open(photoTitle, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_AT_END)) {
sd.errorHalt("opening photoTitle.txt for write failed");
}
SendTakePhotoCmd(); //take photo
delay(200); //delay to make sure there is no drop in the data
while(cameraSerial.available()>0) {
incomingbyte=cameraSerial.read(); //clear unneccessary serial from camera
}
byte b[32];
while(!EndFlag) {
j=0;
k=0;
count=0;
SendReadDataCmd(); //command to get picture from camera
delay(75); //delay necessary for data not to be lost
while(cameraSerial.available()>0) {
incomingbyte=cameraSerial.read(); //read serial from camera
k++;
if((k>5)&&(j<32)&&(!EndFlag)) {
b[j]=incomingbyte;
if((b[j-1]==0xFF)&&(b[j]==0xD9))
EndFlag=1; //when end of picture appears, stop reading data
j++;
count++;
}
}
for(j=0;j<count;j++) { //store picture into file
if(b[j]<0x10)
myFile.print("0");
myFile.print(b[j], HEX);
}
myFile.println();
}
StopTakePhotoCmd(); //stop this picture so another one can be taken
EndFlag = 0; // reset flag to allow another picture to be read
myFile.close(); //close file
picCnt++; //increment value for next picture
}
//Send Reset command
void SendResetCmd() {
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x56);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x26);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
}
//Send take picture command
void SendTakePhotoCmd() {
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x56);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x36);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x01);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
a = 0x0000; //reset so that another picture can taken
}
void FrameSize() {
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x56);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x34);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x01);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
}
//Read data
void SendReadDataCmd() {
MH=a/0x100;
ML=a%0x100;
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x56);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x32);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x0c);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x0a);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)MH);
cameraSerial.write((byte)ML);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x20);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x0a);
a+=0x20;
}
void StopTakePhotoCmd() {
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x56);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x00);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x36);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x01);
cameraSerial.write((byte)0x03);
}
Python
The Python code from the camera tutorial has been revamped to allow for multiple photos to be processed at a time. This is set up to work with the naming given in the above code. The user may still have to adjust the range depending on the number of photos.
#!/usr/bin/python
# open file
import binascii
count = 0
for count in range (0,4):
f = open ("PIC%d.txt" % (count),"r")
nf = open("IMAGE%d.jpg" % (count),"wb")
#Read whole file into data
while 1:
c = f.readline()
d = c.strip()
#print (c)
#print (d)
if not c:
break
nf.write(binascii.a2b_hex(bytes(d, "ascii")))
# Close the file
f.close()
nf.close()